Alfa romeo 6C 2500 One of the first cars with mechanical fuel injection
Fuel injection systems require a large amount of sensors to ensure proper operation, these sensors make sure that the right amount of fuel is being delivered at the right time, here are some examples:
What is the Electronic control unit and how does it work?
The Electronic control unit serves as the control center for all of the sensors on a car. The engine control unit is responsible for monitoring and controlling all the sensors on a cars engine. The ECU monitors the performance of the engine and makes adjustments according to where the problem is. The ECU also does calculations of pulse length (injector time opening) and adjustments to any change in the engine. The ECU can be upgraded and programmed to enhance the performance of the engine.
The mass air flow sensor is a device that is used in conjunction with an oxygen sensor to accurately measure the flow of air into a fuel injection engine. The air flow sensor sends this data to the ECU and it calculates how long the pulse wave should be, this is the amount of time the injector is open regulating the amount of fuel sent to the engine. There are a few ways to measure air flow, the most common in fuel injection engines is the Vane meter sensor and the hot wire sensor. the vane meter uses a spring attached to a potentiometer which measure the voltage and air flow is calculated by the ECU. The hot wire type uses a wire suspended in the engines air stream, an electrical current through the wire heats it up and the air flow cools it down the air flow is calculated by the ECU using the current required to keep the wire at a stable temperature.
This is a hot wire type sensor
What is the air temperature sensor and how does it work?
The air Temperature sensor is used to measure the temperature of the incoming air in the engines air stream. Warm air is less dense than cold air which means more fuel needs to be added to maintain the air/fuel mixture. The ECU measure the temperature and density of the air and adjust the fuel delivery accordingly.
Air temperature sensor
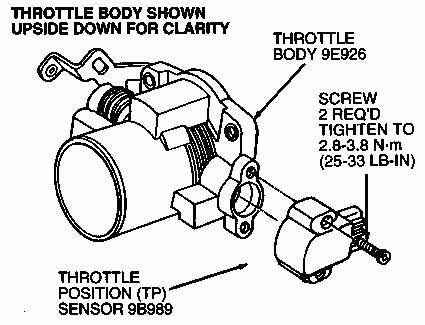
What is the purpose of the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) and how does it work?
The purpose of the throttle position switch is to relay the position of the the throttle butterfly valve to the ECU. A potentiometer on the butterfly valve measures what position it is in by providing resistance when the valve is opening, the more the valve opens the more the resistance. The ECU monitors this resistance and is able to monitor the position of the valve. The ECU can now keep other sensors on the engine in sych with the opening of the throttle valve. If the valve is opened rapidly more fuel can be injected to prevent the engine from stalling.
Throttle position sensor mounted on throttle body
What is the purpose of the throttle body and how does it work?
The throttle body is a part of the air intake system on a fuel injection engine. The body acts as control for the amount of air entering the engine, by metering the air flow with a butterfly valve called the throttle plate. This valve is connected to the throttle pedal via a wire. The butterfly valve is opened and closed by the wire which allows more or less air into the engine.On a single point fuel injection engine the single injector is positioned inside the throttle body.
What is the purpose of the Temperature sensor and how does it work?
There are various temperature sensors in a fuel injection engine, their purpose is to measure the temperatures of fluids or parts in the engine and report it to the ECU. There are temperature sensors for coolant, air, oil, water and more. The sensors work by recording the temperature and relaying that temperature to the ECU, the ECU can now make adjustments to decrease or increase the temperature of the fluid. An engine has a optimum running temperature which is maintained by the ECU.
What is the purpose of the fuel rail?
The Fuel rail is a part found on electronic fuel injection engines, its purpose is to provide fuel to the individual cylinder injectors, it also provides a seat for the injector. Fuel is pumped into the rail through a regulator and the right amount of fuel is released by the injectors, if there is too much pressure in the fuel rail then the regulator releases pressure with a return valve.
Fuel rail with injectors
What is the purpose of the fuel pressure regulator and how does it work?
A EFI engine needs a constant fuel pressure in the fuel rail to feed the injectors, the purpose of the fuel pressure regulator is to maintain that pressure. It controls the pressure and releases pressure when it is high.
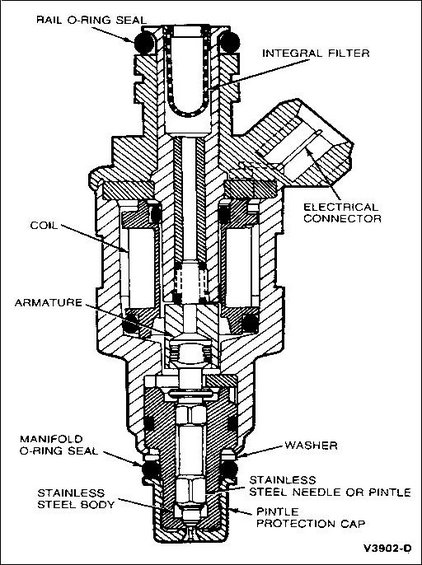
What is the purpose of Fuel injectors and how do they work?
Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering an accurate amount of fuel to the engine from the fuel rail or lines. Injectors need to respond to changes in engine loading by entering more or less fuel in the engine, for this they are connected to the ECU which monitors engine loading and changes the injectors pulse width. this pulse width is the length of time that the injectors are open for. There are different types of injectors like indirect and direct injection. Indirect places the injectors in the intake manifold and fuel is sprayed just before the intake valve is opened, direct injection means the injectors are positioned in the combustion chamber, High pressure injectors spray fuel directly into the cylinder, this is usually used on diesel engines. There are also mechanical and electronic fuel injection systems, in mechanical fuel injection a high pressure pump is used to pump fuel to the injectors when the fuel pressure in the injector is high enough the fuel overcomes a spring system and is injected into the cylinder. In EFI engines a solenoid in the injector which is controlled by the ECU opens the injector at the right time and for the right amount of time. Different spray patterns are also used on injectors to increase combustion efficiency.
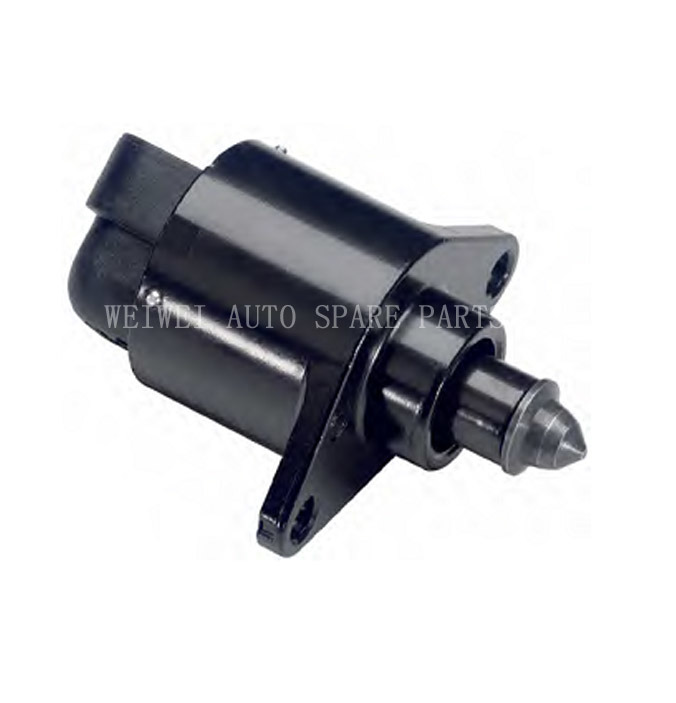
What is the idle air control valve and how does it work?
The idle air control valve controls the amount of air entering the engine while idling. The valve is positioned in the throttle body and opens to allow air to bypass the throttle plate when idling and closes when the engine is under load. The ECU controls the opening of the valve this helps regulate the idle speed.
What is the purpose of the oxygen sensor and how does it work?
In all internal combustion engines the right amount of fuel/air ratio is necessary for proper combustion. The oxygen sensor is a device positioned in the exhaust stream which is tasked with measuring the make up of the exhaust whether it is running too lean or too rich. It works in conjunction with other sensors in the engine like the air flow sensor to measure the air/fuel ratio. This information is then sent to the ECU and changes in fuel/air intake are made. The sensor is essentially a voltmeter the amount of fuel in the air/fuel mix changes the voltage, a rich mixture brings a voltage build up, and a lean mixture causes a low voltage.
What is the purpose of the MAP sensor and how does it work?
The purpose of the MAP sensor or Manifold absolute pressure sensor is to provide information about the air pressure in the intake manifold to the ECU. The ECU can use this data to calculate the density of the air in the system, and in turn calculate the amount of fuel needed to achieve efficient combustion. The MAP sensor is placed on or above the intake manifold, it essentially operates as a barometer.
What is the purpose of the plenum chamber and how does it work?
The plenum chamber in internal combustion engines is a chamber situated between the throttle body and attached to the intake manifold, it's purpose is to act as a stabiliser for air flow into the engine. Air intake pulses inside the intake manifold as air is only need on 1 of four strokes, the plenum chamber helps maintain constant air flow by storing air for the next intake and helps dampen the pulsing effect.
What is the purpose of the Crankshaft sensor?
The crankshaft sensor is used to relay the position and speed of the crankshaft to the ECU. Using the data from the crank sensor the ECU can control the ignition and other aspects of engine timing. The crank sensor can also relay the speed of the engine in RPM to the ECU.
What is the purpose of the camshaft sensor?
The Camshaft sensor works on similar principles to the crankshaft sensor. It measures the position and speed of the camshaft to aid the ECU in engine timing.
Explain how Single and Multi injection systems work?
In a Fuel injected engine the fuel is delivered to the intake manifold via injectors. In a single point injection system one injector is positioned inside of the throttle body and provides the fuel for all of the cylinders. This system was used earlier in the development of fuel injection when carburettor engine designs were given small modifications to incorporate the throttle body for fuel injection. Many modern engines use multi point fuel injection, this type of injection has a injector for every cylinder, these injectors are opened by the ECU at the right time. They can be sequential meaning that the injectors open before intake or simultaneous meaning they open all at the same time.









Again, good effort with your work and detail.
ReplyDelete